Enterprise networking has changed dramatically over the last few years. Applications have moved to the cloud, users are working from anywhere, and cyber threats are becoming more frequent and complex. While SD-WAN has played a critical role in modernizing enterprise connectivity, it was never designed to handle today’s cloud-first and security-driven environments on its own.
This shift has accelerated the move toward SASE (Secure Access Service Edge) a unified architecture that combines networking and security into a single, cloud-delivered model. As a result, enterprises are now moving beyond standalone SD-WAN toward integrated SD-WAN and SASE solutions.
Table of Contents
Why Standalone SD-WAN Is No Longer Enough
SD-WAN transformed WAN architectures by replacing expensive MPLS links with intelligent, software-driven connectivity. It enabled application-aware routing, centralized management, and better utilization of broadband links.
However, enterprise requirements have evolved.
Today’s challenges include:
- Heavy dependence on SaaS and cloud applications
- A rapidly growing remote and hybrid workforce
- Increasing security risks at branch and edge locations
- Complex security stacks made up of multiple point solutions
In many deployments, SD-WAN still relies on external firewalls, secure web gateways, and VPNs, resulting in fragmented architectures and higher operational overhead. Traffic is often backhauled to data centers for security inspection, increasing latency and hurting application performance. This is where SASE becomes critical.
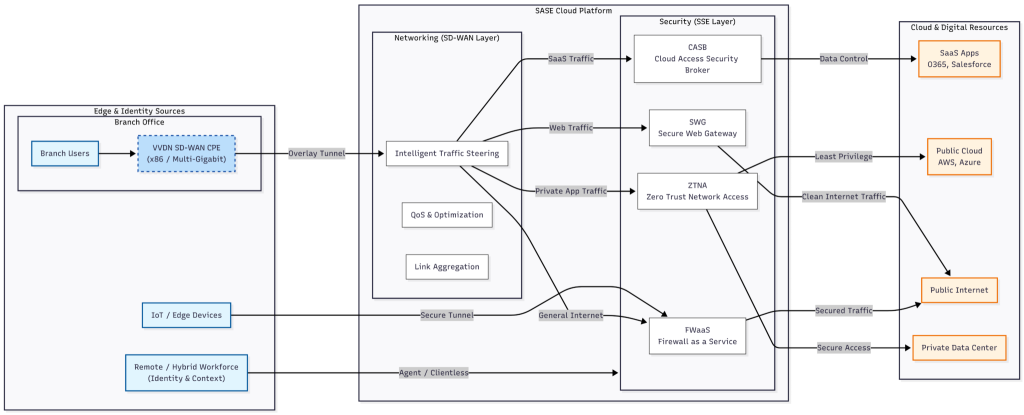
Understanding SASE: Networking and Security at the Edge
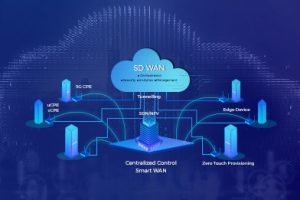
SASE is a cloud-native framework that brings WAN connectivity and security services together. Instead of treating networking and security as separate layers, SASE integrates them and delivers both from the cloud edge.
A typical SASE architecture includes:
- SD-WAN for intelligent traffic routing
- Secure Web Gateway (SWG)
- Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
- Firewall as a Service (FWaaS)
All these services are delivered through globally distributed cloud points of presence (PoPs), close to users and applications.
Key Trends Driving the Shift from SD-WAN to SASE
1. Cloud and SaaS-Centric Enterprises
Enterprises today access applications directly from the internet rather than from centralized data centers. SASE enables secure, direct access to SaaS and cloud workloads without inefficient backhauling.
2. Remote and Hybrid Work as the New Normal
Traditional WAN models were branch-centric. SASE is user-centric, providing secure access based on identity, device posture, and context — regardless of location.
3. Zero Trust Security Adoption
Enterprises are moving away from perimeter-based security. SASE supports Zero Trust principles, ensuring continuous verification and least-privilege access.
4. Need for Simplicity and Scalability
Managing multiple security appliances and licenses is complex. SASE simplifies operations by offering policy-driven, cloud-managed security and networking.
Business and Technical Advantages of SASE
Unified Architecture
SASE reduces complexity by combining WAN and security into a single platform. Enterprises gain better visibility, simpler management, and faster troubleshooting.
Better Application Performance
By enforcing security closer to users, SASE reduces latency and improves performance for cloud and SaaS applications.
Consistent Security Everywhere
Security policies are applied uniformly across branches, remote users, and cloud environments, improving compliance and reducing risk.
Scalable and Future-Ready
SASE allows enterprises to scale quickly — adding new sites, users, or services without deploying additional hardware.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership
By consolidating networking and security solutions, enterprises can significantly reduce hardware, licensing, and operational costs.
SD-WAN Remains the Foundation of SASE
Despite the shift, SD-WAN remains a critical building block of the SASE architecture. It provides:
- Intelligent traffic steering
- Link aggregation and optimization
- Quality of Service (QoS) enforcement
- Visibility into application behavior
Modern SASE solutions rely on high-performance SD-WAN CPE platforms at the edge, often built on x86-based architectures for flexibility and scalability.
Conclusion
VVDN’s SASE offering combines high-performance SD-WAN CPE hardware with SASE-ready edge architecture to support integrated networking and security services. VVDN designs and engineers SASE-capable edge platforms that can host virtualized security functions such as firewall, secure web gateway, and zero-trust access, while seamlessly integrating with cloud-delivered SASE frameworks from ecosystem partners. With hardware acceleration, multi-gigabit throughput, and software-upgradable designs, VVDN enables OEMs and service providers to deploy SASE-enabled WAN solutions that scale securely and evolve with changing enterprise requirements.