The continuous transformation of networking technology has always been a lifeline behind many innovations, globalization, and the connected world. Access Networks are evolving by leaps and bounds to support the growing needs of technological space. Covid-19 has also put extra stress on scalability, manageability, and security on Access Networks, increasing the need to evolve faster than ever before. Using the old approach to support new needs such as high levels of mobility, distributed devices in work from home scenarios, a large number of network deployments, etc. are difficult to maintain and secure, which results in an expensive, complex global connectivity landscape. This leads to a cumbersome cycle of patching, updating, and bug fixing which requires skilled resources and heavy cost. These cumbersome networks create good time opportunities for hackers. Using alternate secure communication methods such as MLPS is also very expensive with the additional burden of long lead times for deployment to new locations. Hence, companies are now looking for a centrally managed network that should be easily scalable, reliable-by taking less setup time, secured, and cost-efficient, thereby reducing the burden on the IT services. All these above points have been realized by SD-WAN.
What is SD-WAN?
As the name signifies, a software-defined wide-area network uses the software to define the policies, management, security between your branches and remote device deployments like work from home scenarios with cloud instances. A typical SD-WAN setup means separating the data plane from the control plane, replacing Internetworking protocols with APIs makes it possible.
Each router has a data plane containing the information and a control plane, which tells the data where and how to go. Unlike in Traditional WAN connectivity where the Data Plane and Control plane lies in end devices, SD-WAN simplifies the network by separating the data plane and the control plane which is now centralized. It means network administrators can write new rules and policies, and then configure and deploy them across an entire network in a fraction of the time required.
Now all the configurations, policies for routing, security measures, and firewalls can be managed and pushed from a common platform to all the configured devices via SD-WAN controllers. The SD-WAN also provides the flexibility to use the existing Infra or hybrid WAN for saving large deployment costs. It can include existing routers and switches all running software with control policy, security, networking functions, and management tools depending on the customer requirements. It also gives the ease to configure, manage and upgrade all the above networking functions. For example, in traditional WANs, it depends on physical routers to connect remote or branch to applications hosted on data centers. And all the traffic needs to be routed through a centralized data center for all the services that put an overload on the centralized infra, making it a complex and costly affair. With the SD-WAN implementation, all the traffic can go directly to end devices/ services hosted on the cloud as per the policies and algorithms set by the control plane on the devices.
SD-WANs also provide the capability to manage multiple WAN’s/Smart WAN management or provide the ability to select the path dynamically between expensive MPLS to cheap broadband & LTE. Certainly, this provides better bandwidth management between the branch offices and helps IT services to reduce heavy load and cost. It also provides simple interfaces for WAN Management and zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) at the branch or home deployments and makes the process of configuring and managing super easy.
The SD-WAN also gets lots of encouragement to use open-source Software and design customized solutions at a relatively low cost. With this, we can integrate 3rd party applications such as firewalls, VPNs, controllers, etc.
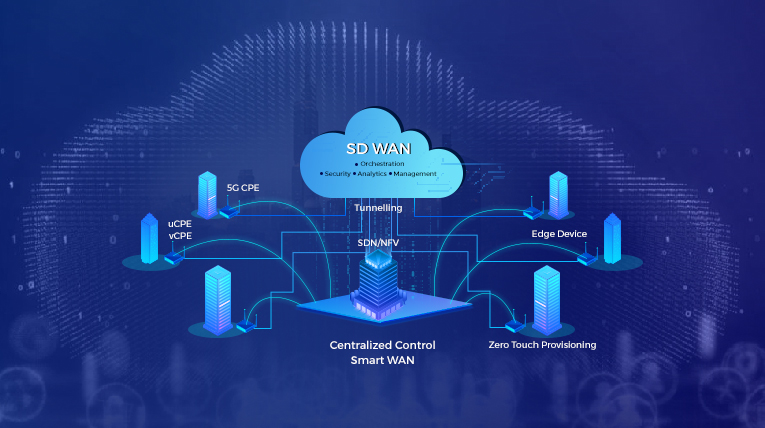
SD-WAN Components and Architecture
The SD-WAN architecture consists of two planes: Data Plane and control plane whose high-level introduction has been covered above. Let’s get to more details about the architecture requirements of these planes. The control plane SD-WAN deployment can be achieved with On-prem-Only, Cloud-enabled, and Cloud-Enabled with the backbone with their own Pros and Cons.
On-Prem-Only
On-Prem-Only architecture is exactly what the name signifies. The company has installed an SD-WAN box (plug n play), which is performing real-time traffic shaping at each location. It is not like some of the other architectures on the cloud perspective, the on-site SD-WAN box does not connect to a cloud gateway. It is the best fit for Companies hosting all their applications in their own IT infra (without any cloud applications). There isn’t a strong need to utilize a cloud-based SD-WAN as it adds cloud costs unnecessarily.
Cloud-enabled
In a cloud-enabled SD-WAN solution, an onsite SD-WAN box is connected to a cloud (virtual) gateway. With this approach, the company gets the benefit of an on-prem-only architecture and increased performance and reliability of cloud applications. The cloud gateway is connected to the cloud providers (i.e. Office 365, AWS, Salesforce, etc.), which results in an improvement in the performance of your cloud apps. If a company’s Internet goes down while using a cloud application, the gateway can keep a cloud session active (while the circuit flaps) and search for other internet circuits. The SD-WAN can re-route that cloud app instantaneously to an alternate Internet circuit, preventing interruption of a single session. It is the best fit for Companies running cloud applications like Office 365, AWS, DropBox, Azure, Salesforce, etc.
Cloud-enabled Plus the Backbone– This architecture offers an on-site SD-WAN box connecting branches to the SD-WAN provider’s nearest network point of presence (POP), where traffic goes to the SD-WAN provider’s network backbone. While the traffic is transmitting on the provider’s private backbone, it is expected to maintain low levels of latency, packet loss, etc. The backbone is also directly connected with major cloud applications (i.e. Office 365, AWS, etc.), and increases the performance and reliability. It is the best fit for a company using real-time network applications and heading towards removing dependency on their MPLS network to reduce costs but does not want their real-time traffic going 100% over the public Internet to check on high latency, packet loss.
The three main components of all the above deployments are
- SD-WAN Edge Device/CPE – It is the component where the network endpoints reside. The data plane activities are performed in the edge device. The orchestrator can push the microservices in docker/container carriers for configuring the device as per the requirements. These devices can be a branch office, a remote data center, or a cloud platform.
- SD-WAN Orchestrator– It is a virtualized manager for the network on the control plane and applies the protocols and policies on the traffic.
- SD-WAN Controller – It centralizes management, enabling operators to see the full network in a single platform, and sets policy for the orchestrator to execute.
Benefits of SD-WAN
- Cost – SD-WANs reduce the overall cost of implementation. When we talk about SD-WAN devices, they will be lighter with fewer capabilities because most processes in the control plane now happen on the centralized Cloud and that can be achieved with existing devices or new low-end devices.
Bandwidth costs by using less expensive services, such as broadband whenever possible. The dedicated Internet access (DIA) for higher uptime and performance can also be used. And by smart management, the dependency on MPLS can be reduced and save cost.
- Time – The setup and management time will decrease significantly. Because of the centrally managed and zero-touch provisioning devices that require minimum efforts to deploy and manage.
- Performance – Cloud and Internet performance also improve because of low data latency and packet loss. Now devices can be connected directly to the cloud without approaching the data centers. Applications or QoS services can be prioritized to provide a better experience for end-users.
- Security & Control: Network traffic is encrypted and the network is segmented to improve security. All the security policies can be pushed and deployed to all infra in a fraction of time and manage, control, feedback becomes super easy.
- Flexibility: Customize the bandwidth required as per the QoS, regular updates, and upgrades from a single point of control.
- Scalable: As you grow, scaling up the deployments is super easy and requires fewer skills. The scalability is well satisfied with SD-WAN networks.
How VVDN help OEMs to get the SD-WAN
VVDN helps customers transform to SDN / NFV by an end-to-end software framework development, system engineering, and integration to develop future-proof networks at the best price-performance ratio. We help to develop the ideal SD-WAN product which helps in reducing the complexity and criticality of IT dependency for rapidly scaling networks, minimize disruptive technology adoption risks, and reduces Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). VVDN helps in designing and developing robust enterprise Smart WAN networks that are optimized for growing needs. VVDN provides multi-Cloud architectures including private and public clouds.
VVDN Helps OEM’s With Complete WLAN Software Development, Application Development, Private Or Public Cloud Development Services with Off-the-shelf CPE Equipment, and Manufacturing Support.
Few highlights about VVDN’s offerings are:
- Customized White Box Platforms
- Cloud/On-premises Controller
- Integration Of 3rd Party VNFs
- Hybrid-WAN Designs
- Zero Touch Deployment
- Tunneling (IPsec, EoGRE, and other 3rd party integrations)
- OPD, Intel DPDK Integration
- OVS Customization
For more info on SD-WAN offerings please click here.